Origin and Termination of Internal Carotid Artery
Internal carotid artery is one of the two terminal branches of common carotid artery. It supplies structures present in the cranial cavity and orbit. Its branches anastomose with the branches of external carotid artery in the scalp and face and middle ear.
Origin: It begins at the upper border of the lamina of thyroid cartilage (level of disc between C3 and c4 vertebra).
Termination: It terminates in the cranial cavity at the base of brain by dividing into its terminal branches viz. anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
Course of Internal Carotid Artery
Course: The course of internal carotid artery is divided into 4 parts i.e. Cervical, Petrous, Cavernous and Cerebral.
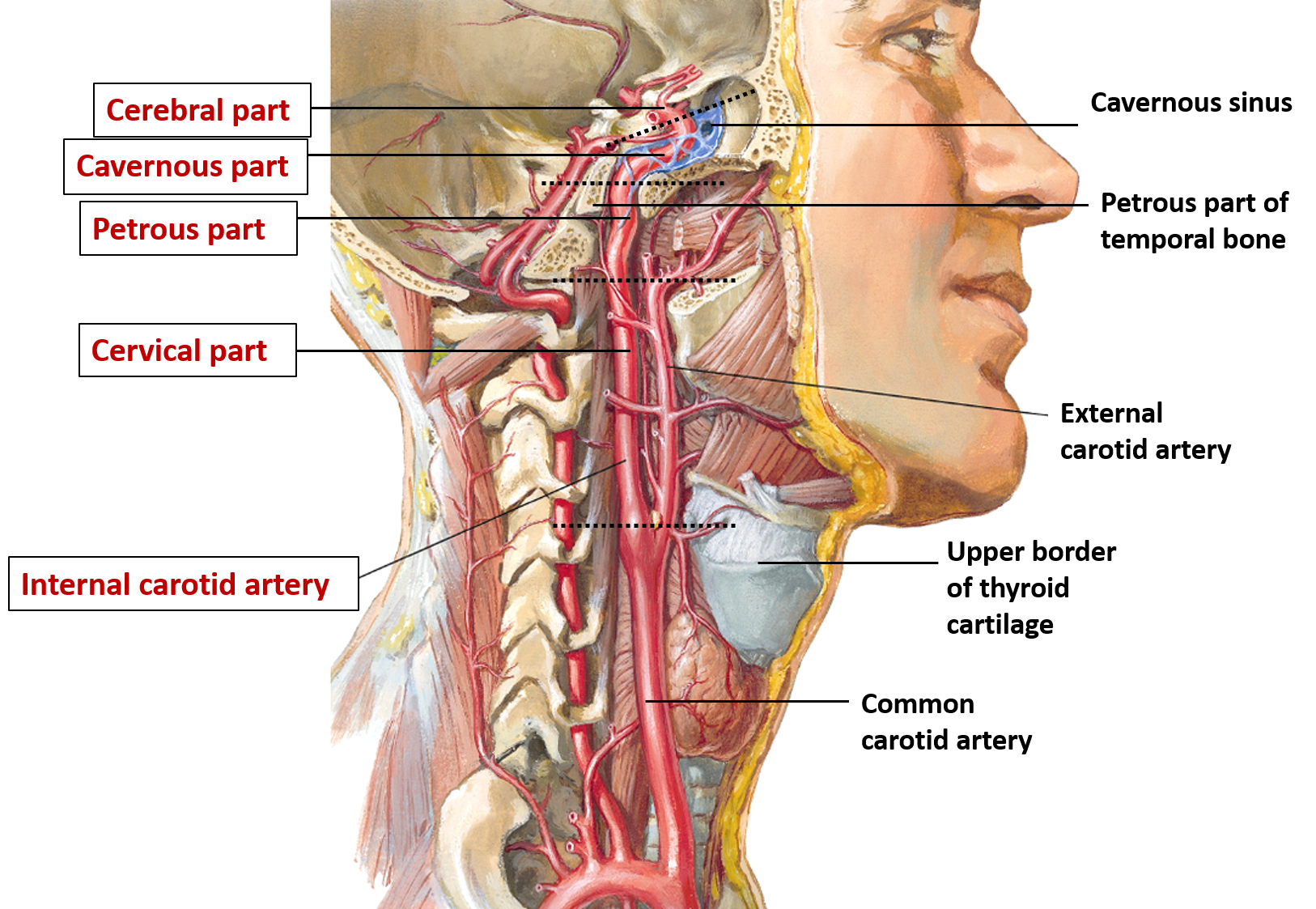
Cervical part
- The cervical part of the internal carotid artery undergoes a straight course in the neck from its origin up to the base of skull.
- It ascends up in the carotid sheath along with internal jugular vein (lateral to the artery) and vagus nerve (posterior to artery) in the carotid triangle. Here the artery is superficial and is covered by sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- The artery then leaves the carotid triangle by passing deep to the posterior belly of digastric muscle. In its upper part it lies deep to the parotid gland and styloid process along with structures attached to it and lies anterior to the transverse processes of the upper three cervical vertebrae.
- In the upper part the structures that pass between the internal and external carotid arteries are:
- Styloglossus muscle
- Stylopharyngeus muscle
- Tip of the styloid process
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve
- It reaches the base of skull and here the internal jugular vein lies posterior to it and the the last four cranial nerves i.e. glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory, and hypoglossal are located in between the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery.
- In its course , it is surrounded by carotid plexus, derived from the superior cervical ganglion of the sympathetic trunk.
Petrous part
- This part of internal carotid artery passes through the carotid canal located in the petrous part of the temporal bone. It enters the carotid canal through the lower opening at the base of skull.
- It first ascends a short distance, then curves forward and medially and again ascends as it leaves the canal to enter the cranial cavity.
- The artery lies anterior to the tympanic cavity and below the auditory tube.
Cavernous part
- The artery enters the cranial cavity through the upper (anterior) opening of the carotid canal, located in the posterior wall of foramen lacerum.
- It enters the cavernous sinus and then passes forwards and ascends again to pierce the dural roof of the sinus to reach the under surface of cerebrum.
- Within the cavernous sinus it is related to the abducent nerve inferolaterally. It lies outside the endothelial lining of the cavernous sinus.
Cerebral part
- It turns backwards above the roof of cavernous sinus and then turns upwards by the side of optic chiasma to reach the anterior perforated substance. Here it divides into anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
♦The curve of the internal carotid artery in the cavernous sinus and above it (U-shaped bend) is called the carotid siphon which perhaps dampens down the pulsation of the artery and maintain a regular flow to the brain.
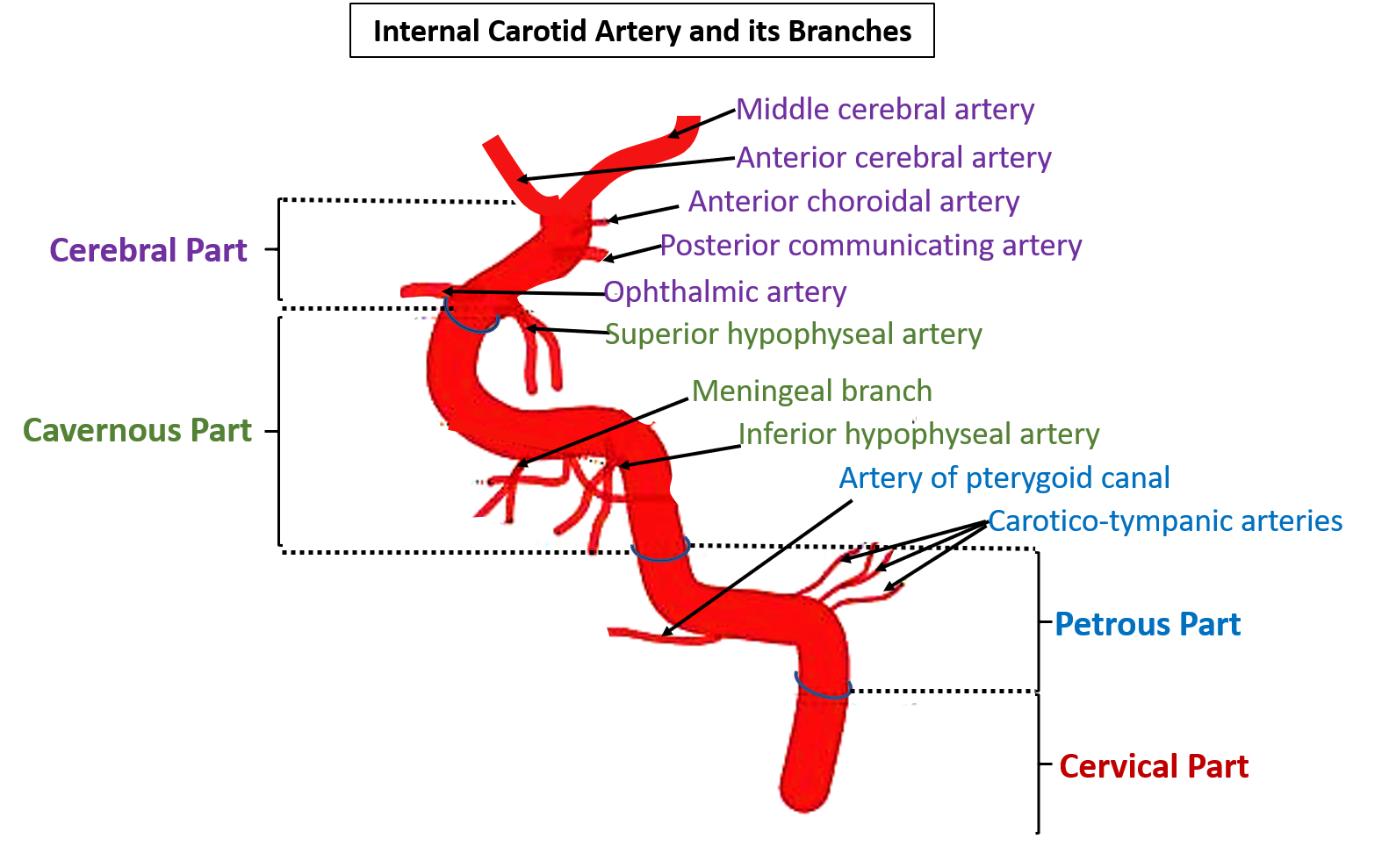
Branches of Internal Carotid Artery
Following are the branches of Internal carotid artery:
From the cervical part: None
From the Petrous part
- Caroticotympanic branches to the middle ear:
- These branches anastomose with the anterior and posterior tympanic arteries ( br. of maxillary ( br. of external carotid))and stylomastoid ( br. of posterior auricular -> br. of external carotid) arteries respectively.
From the cavernous part
- Meningeal branch
- Superior and inferior hypophyseal arteries to the pituitary gland.
From the cerebral part
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Middle cerebral artery
- Anterior choroidal artery
- Posterior communicating artery
- Ophthalmic artery
Sites of anastomosis between branches between branches of Internal carotid and External carotid arteries.
- Scalp: Between supratrochlear and supraorbital (branches of ophthalmic artery -> internal carotid artery) and superficial temporal posterior auricular and occipital arteries (branches of external carotid artery).
- Face: between the dorsal nasal branch of ophthalmic artery and the terminal branch of facial artery establishes a collateral circulation between the internal and external carotid arteries.
- Middle ear: Caroticotympanic branches of internal carotid artery anastomose with the anterior and posterior tympanic arteries ( branches of maxillary ( branches of external carotid))and stylomastoid ( branch of posterior auricular -> branch of external carotid) arteries respectively.
Applied Aspect
The posterior communicating branch of internal carotid artery connects it with the posterior cerebral artery, a branch of vertebrobasilar system and forms the Circle of Willis. This arterial circle forms an important collateral circulation to brain in the event of obstruction.
