Advertisements
What is the origin and root value of radial nerve?
Origin: Is the largest nerve of the brachial plexus. It arises from posterior cord of brachial plexus.
Root Value: Its root value is C5– T1 spinal segments of spinal cord .:
Describe the course of radial nerve?
- It arises from the posterior cord of brachial plexus in the axilla
- It enters the posterior compartment of arm at lower border of the teres major through the lower triangular space.
- It then lies in the spiral groove of humerus along with the profunda brachii vessels between the lateral and medial heads of triceps.
- At the lower end of the spiral groove it pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior compartment of arm.
- It then enters the cubital fossa and at the level of lateral epicondyle it terminates by dividing into superficial and deep (posterior interosseous ) branches.
- The superficial branch enters the forearm and runs deep to brachioradialis.
- In the lower 1/3rd of the forearm it winds around the lateral aspect of radius to reach the anatomical snuff box on the dorsum of hand.
- It terminates by dividing into digital branches.
- The deep (posterior interosseous nerve) branch leaves the cubital fossa by passing through the supinator to enter the posterior compartment of forearm.
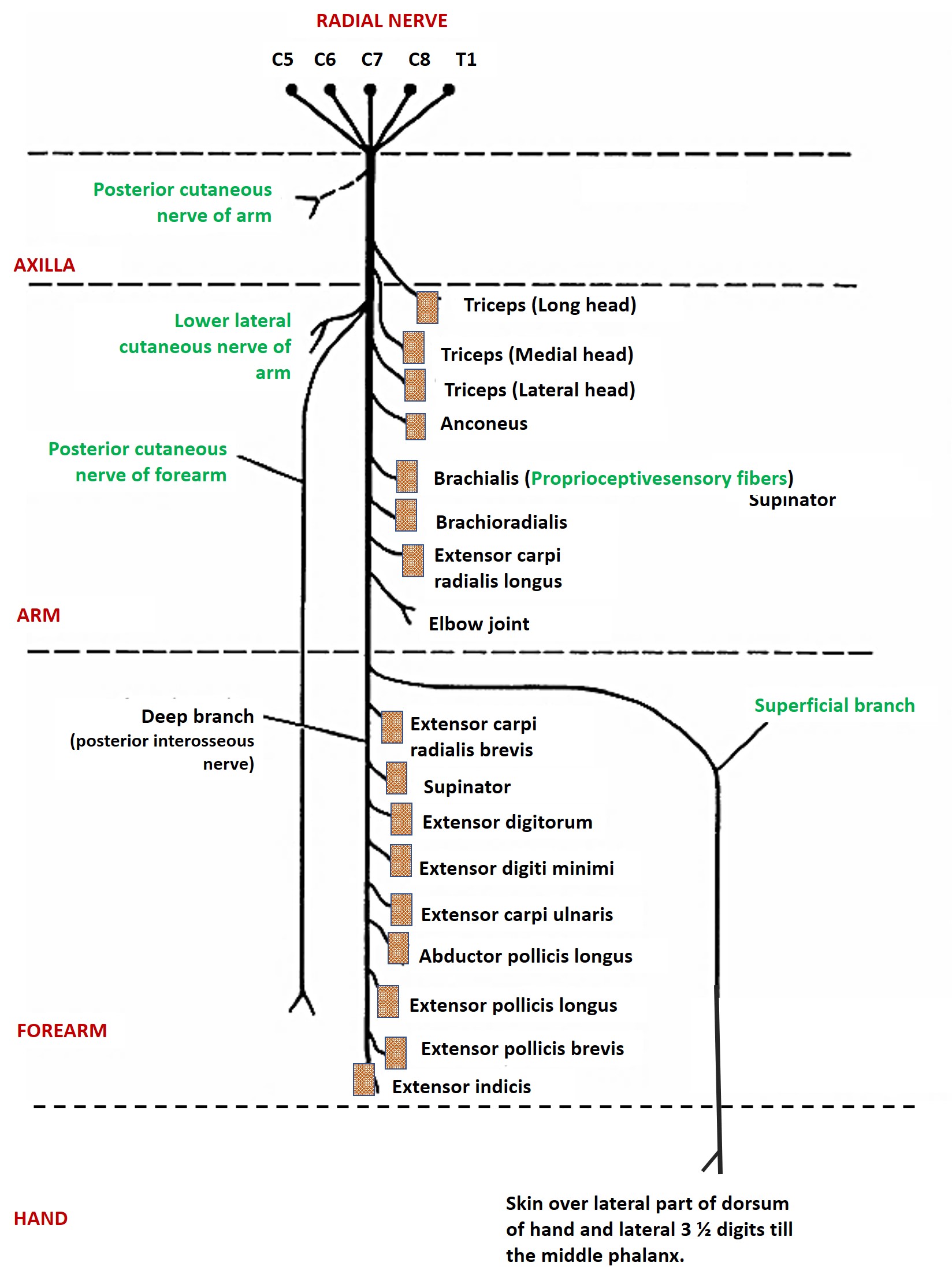
Name the branches and structures supplied by radial nerve?
Branches and distribution:
- In the axilla
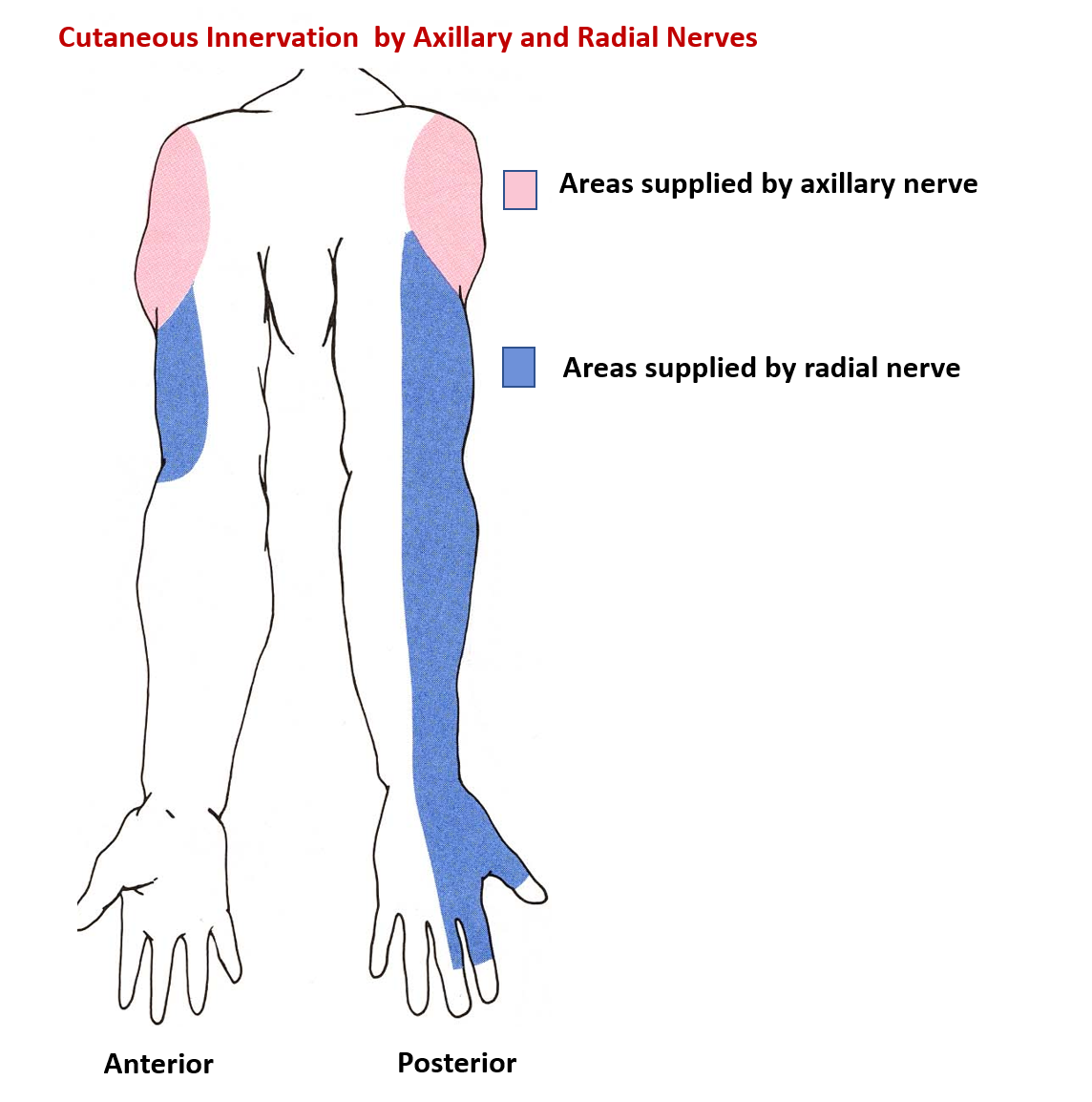
- Sensory branch: Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm ( supplies skin on the back of arm)
- Motor branches:
- Nerve to long head of triceps
- Nerve to medial head of triceps
- In the spiral groove:
- Sensory branches:
- Lower lateral cutaneous nerve of the arm ( skin on the lateral surface of arm)
- Posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm ( skin of the middle of the back of forearm)
- Motor branches:
- Nerve to lateral head of triceps
- Nerve to medial head of triceps
- Nerve to anconeus
- Sensory branches:
- In the anterior compartment of arm:
- Motor branches:
- Nerve to brachialis (proprioceptive)
- Nerve to brachioradialis
- Nerve to extensor carpi radialis longus
- Motor branches:
- In the cubital fossa (Terminal branches):
- Superficial branch (sensory branch)
- Innervates the skin over the lateral part of the dorsum of hand and dorsal surface of lateral 3 ½ digits upto the middle phalanx.
- Deep (posterior interosseous) branch (motor branch)
- In the cubital fossa:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- Supinator
- In the posterior compartment of forearm
- All the extensor muscles of forearm (extensor digitorm, extensor indicis, extensor digiti minimi, externsor carpi ulnaris, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis longus and extensor pollicic brevis)
- In the cubital fossa:
- Superficial branch (sensory branch)
Applied Aspect
Radial nerve lesion
The lesion of radial nerve leads to wrist drop (loss of extension of wrist due to paralysis of extensors of wrist). The radial nerve may get injured at the following two sites:
In the axilla:
- Due to pressure of upper end of crutches ( cruch palsy)
- Drunkard falling asleep with the arm pressing over the back of chair ( Saturday night palsy)
- Injury of radial nerve in the axilla results in :
- Loss of extension at elbow joint.
- Wrist drop ( loss of extension of wrist due to paralysis of extensors of wrist).
- Loss of extension of digits.
- Sensory loss on the skin over the posterior surface of lower part of arm, middle of the posterior part of forearm , lateral part of dorsum of hand and dorsal surface of lateral 3 ½ digits.
In the spiral groove:
- Midshaft fracture of humerus
- Injury to radial nerve at this site results in:
- Wrist drop
- Loss of extension of digits.
- Sensory loss on the skin over the lateral part of dorsum of hand and dorsal surface of lateral 3 ½ digits upto middle phalanges.
- Injury to radial nerve at this site results in:
* Extension of elbow joint is possible because nerves to long and medial heads of triceps arise in the axilla proximal to the site of lesion.

Ma’am please publish a book with the same content on this website. I have read my whole 1st year only with this website. Now it is difficult to study on phone always. It would be very helpful you could publish it or provide us pdf. Thank you.
Thanks a lot. I am happy you liked it.
Thanks Harsh.
I don’t know how to thank you but you are an absolutely God sent. I love your work and I would 100% buy your book if you were to publish it
Greetings Miss Ponam. I feel very sorry that I can’t comment on every single published answer of yours, but you’ve have done a spectacular work. Absolutely remarkable. God bless you Miss Ponam. Take care.
Thnx a lot.This has clarified my all confusions.