Advertisements
What is the origin and root value of median nerve?
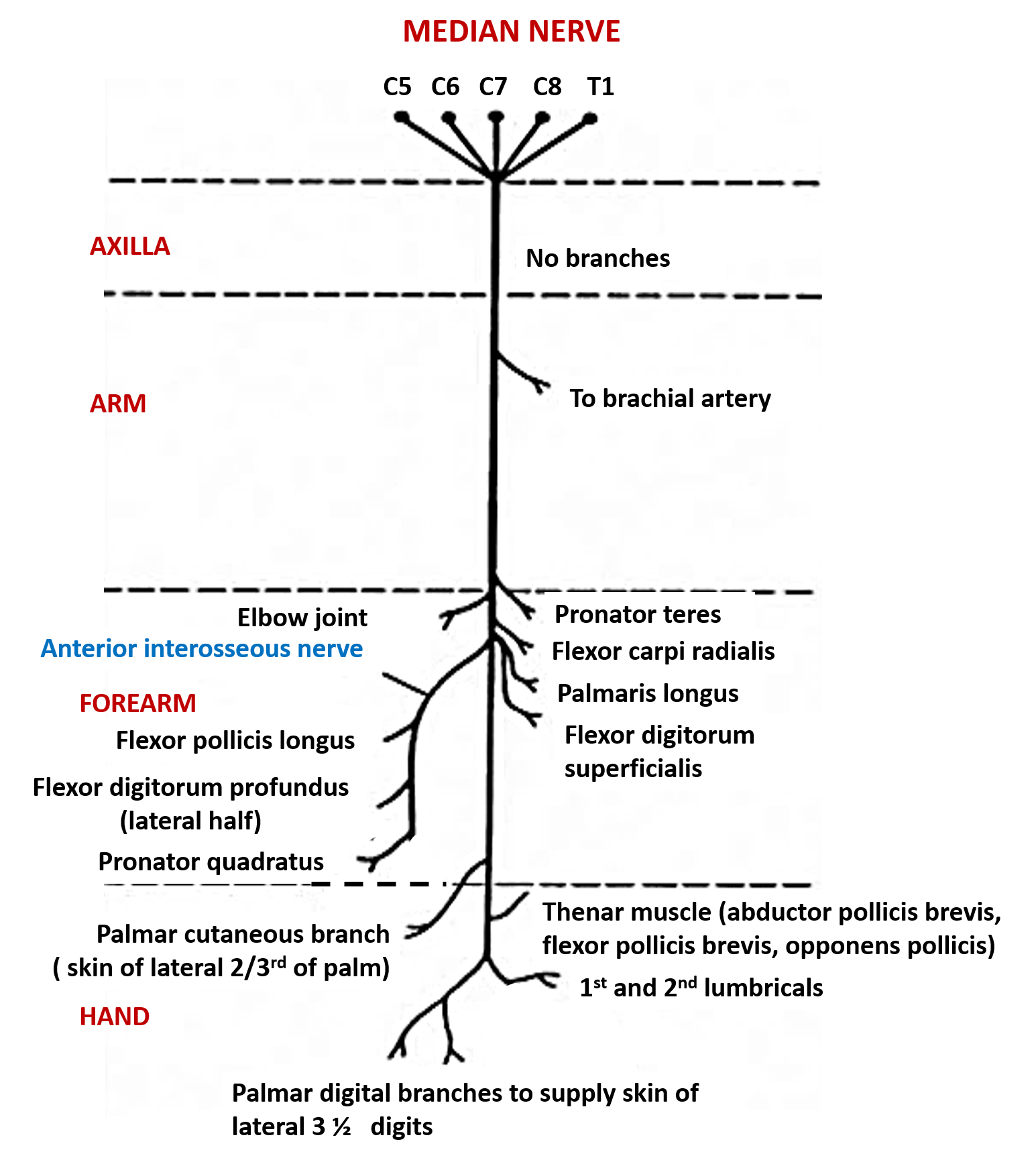
Origin: Median nerve arises in the axilla by two roots ( lateral and medial ) from the lateral and medial cords of brachial plexus.
Root value: Its root value is C5-T1 spinal segments
Describe the course of median nerve.
- Median nerve enters the anterior compartment of arm at the lower border of teres major.
- In the arm, initially it lies lateral to the brachial artery, then crosses in front of the artery to reach its medial side.
- Enters the cubital fossa where it lies medial to the brachial artery.
- It leaves the cubital fossa by passing between the two heads of the pronator teres and gives off anterior interosseous nerve.
- In the forearm , it passes behind the tendinous arch of flexor digitorum superficialis and runs downwards deep to the muscle.
- 5 cm. proximal to flexor retinaculum it becomes superficial and lies lateral to the tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis .
- It then enters the palm through the carpal tunnel (deep to flexor retinaculum) and divides into lateral and medial terminal branches.
Name the branches and structures supplied by median nerve.
Branches and distribution:
- In the axilla and arm : no branches
- In the cubital fossa:
- Gives branches from its medial side to the all the superficial flexors ( pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis) of th
- e forearm except flexor carpi ulnaris.
- In the forearm:
- Anterior interosseous branch supplies 2 ½ muscles:
- Flexor pollicis longus
- Pronator quadrates
- Lateral half of the flexor digitorum profundus.
- Anterior interosseous branch supplies 2 ½ muscles:
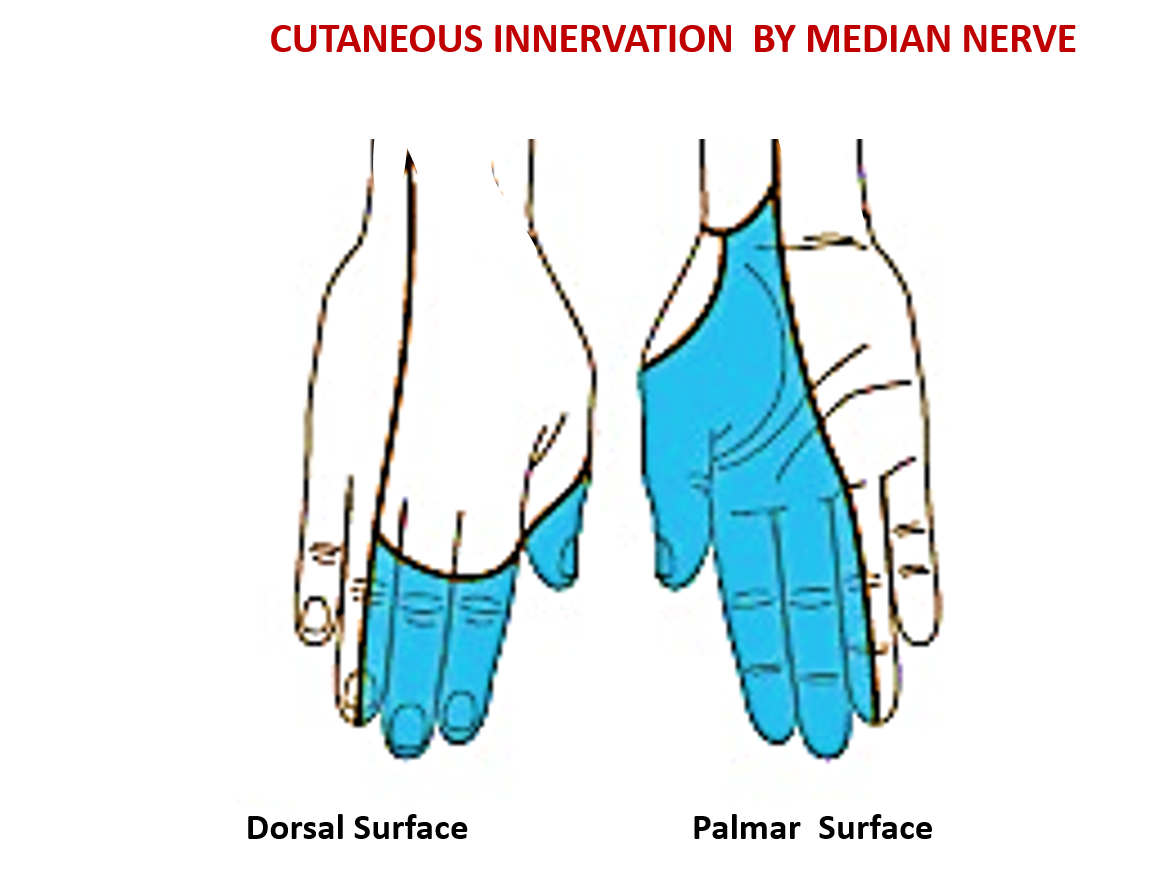
- Before entering carpal tunnel it gives off palmar cutaneous branch ( passes superficial to flexor retinaculum) which supplies skin over thenar eminence and lateral part of palm.
- In the palm:
- Lateral branch gives:
- Motor branches :A recurrent branch that supplies thenar muscles ( abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis) except adductor pollicis.
- Sensory branches: Three palmar digital branches.
- Medial branch gives:
- Sensory branches: Two palmar digital branches.
- Lateral branch gives:
The five palmar digital branches supply the skin of the palmar surface of lateral 3 ½ digits including the nail beds and the skin on the dorsum of the distal phalanx .
Applied Aspect
Median nerve injury
- Median nerve may get injured at the following sites:
- At the elbow :
- due to supracondylar fracture of humerus.
- Entrapment of nerve between the two heads of pronator teres (pronator syndrome).
- Injury to median nerve at this site results in:
- Loss of pronation.
- Weakened flexion at wrist.
- Ape thumb deformity: Thum is laterally rotated and adducted. Opposition of thumb is not possible.
- Thenar eminence is flattened
- Benediction Attitude: when patient tries to make fist the index and the middle finger remain extended due to paralysis of the flexors of these two digits.
- Sensory loss over the lateral half of the palm and lateral 3 ½ digits.
- In the carpal tunnel [Click here]
- At the elbow :

Good notes , esay and easy observation
omg i love this ,students who don’t knw this site must feel lost thank you