What are the components of the cardiovascular system?
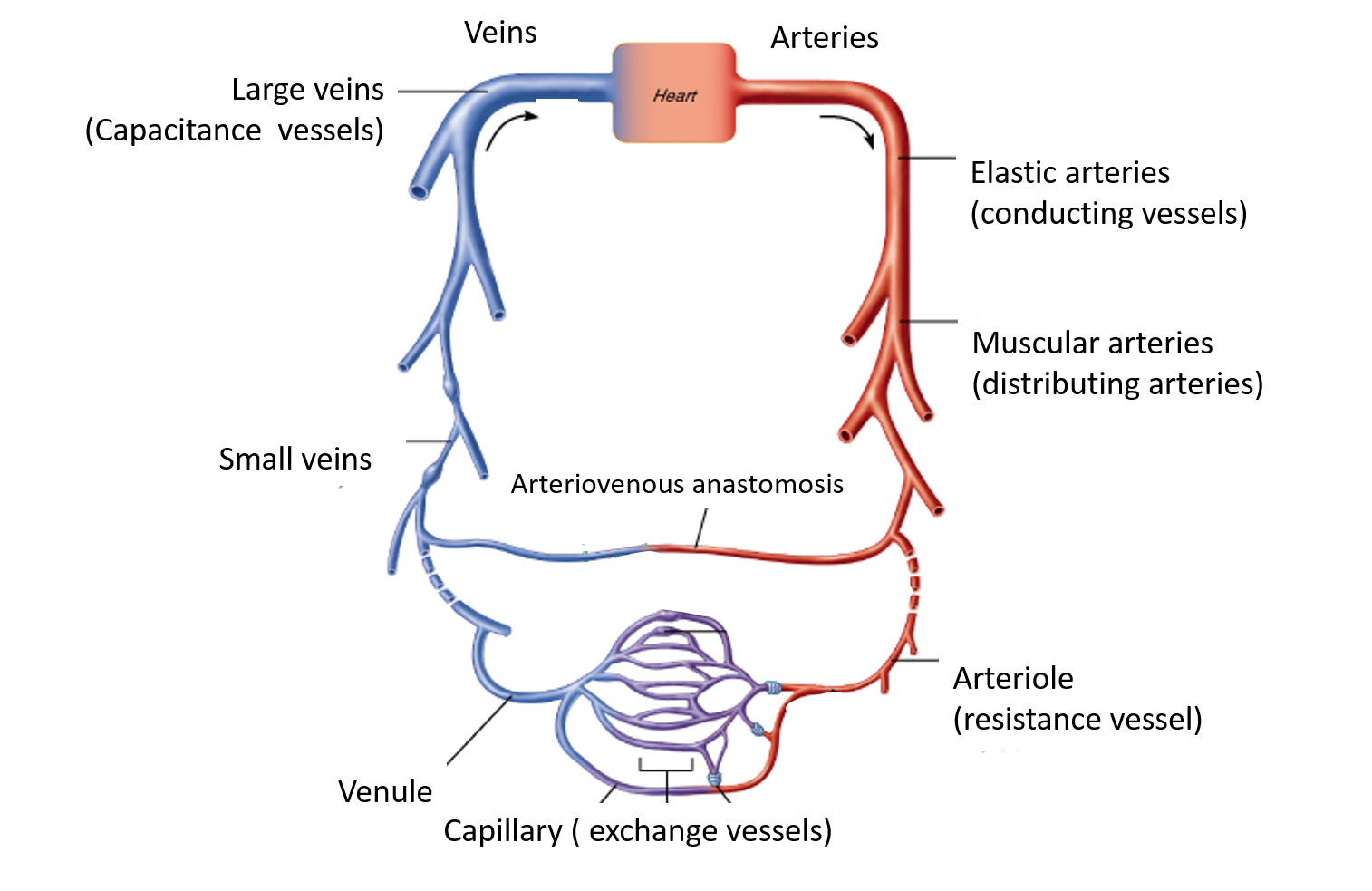
Cardiovascular system includes heart, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules and veins.
Arteries
- Arteries carry blood away from the heart .
- They usually carry oxygenated blood to various organs (except pulmonary arteries – which carry deoxygenated blood to lungs). They are of two types:
- Elastic arteries/ Conducting arteries: They are large-sized arteries which mainly conduct the blood to small arteries. Examples are aorta and pulmonary arteries, brachiocephalic trunk, common carotid, subclavian and common iliac arteries.
- Muscular arteries/Distributing arteries: they are medium sized arteries and they supply various tissues and organs via their branches. Examples are brachial artery, radial artery, profunda femoris artery.
Arterioles/ Resistance vessels
These vessels have a diameter of 50-100µm. They are the main regulators of peripheral vascular resistance. Contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles in their walls alters the blood pressure of arterial flow.
Capillaries/Exchange vessels
They are the smallest vessels, their average diameter is ` 8 µm. They allow transfer of oxygen and nutrients from the blood to the tissues in the body and carbon dioxide and metabolic waste products from the tissues to the blood.
Veins/Capacitance vessels
- They usually carry deoxygenated blood from the various tissues of the body to the heart (exception is pulmonary veins which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart).
- The smallest veins are called venules.
- The veins which accompany muscular arteries (on either sides of artery) are called venae comitantes.
- Some of the veins have valves to prevent reverse flow of blood (especially in lower limb).
Name the Avascular Tissues/Structures.
Following structures are avascular:
- Epithelium
- Epidermis of skin
- Hair
- Nail
- Cornea
- Cartilage
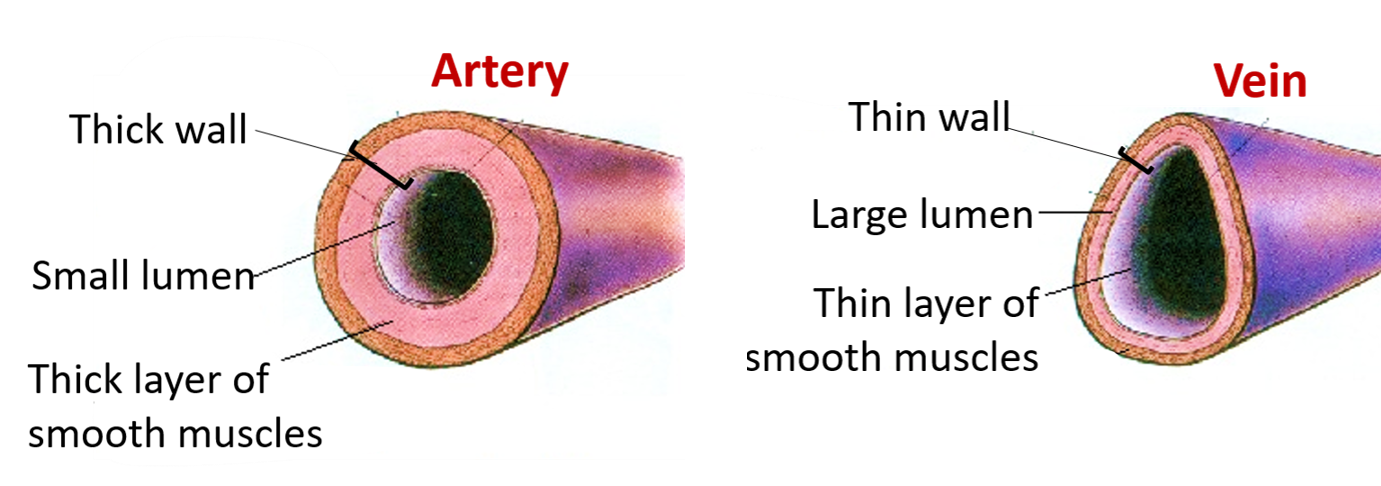
What are the Differences Between the Arteries and Veins?
Following are the differences between the arteries and veins:
| Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|
| Transport blood away from the heart | Transport blood towards the heart; |
| Carry Oxygenated Blood (except in the case of the Pulmonary Artery) | Carry De-oxygenated Blood (except in the case of the Pulmonary Vein) |
| Have relatively narrow lumens; | Have relatively wide lumens . |
| Have relatively more muscle/elastic tissue | Have relatively less muscle/elastic tissue; |
| Transports blood under higher pressure (than veins) | Transports blood under lower pressure (than arteries); |
| Do not have valves . | Have valves to prevent blood flowing in the reverse direction. |
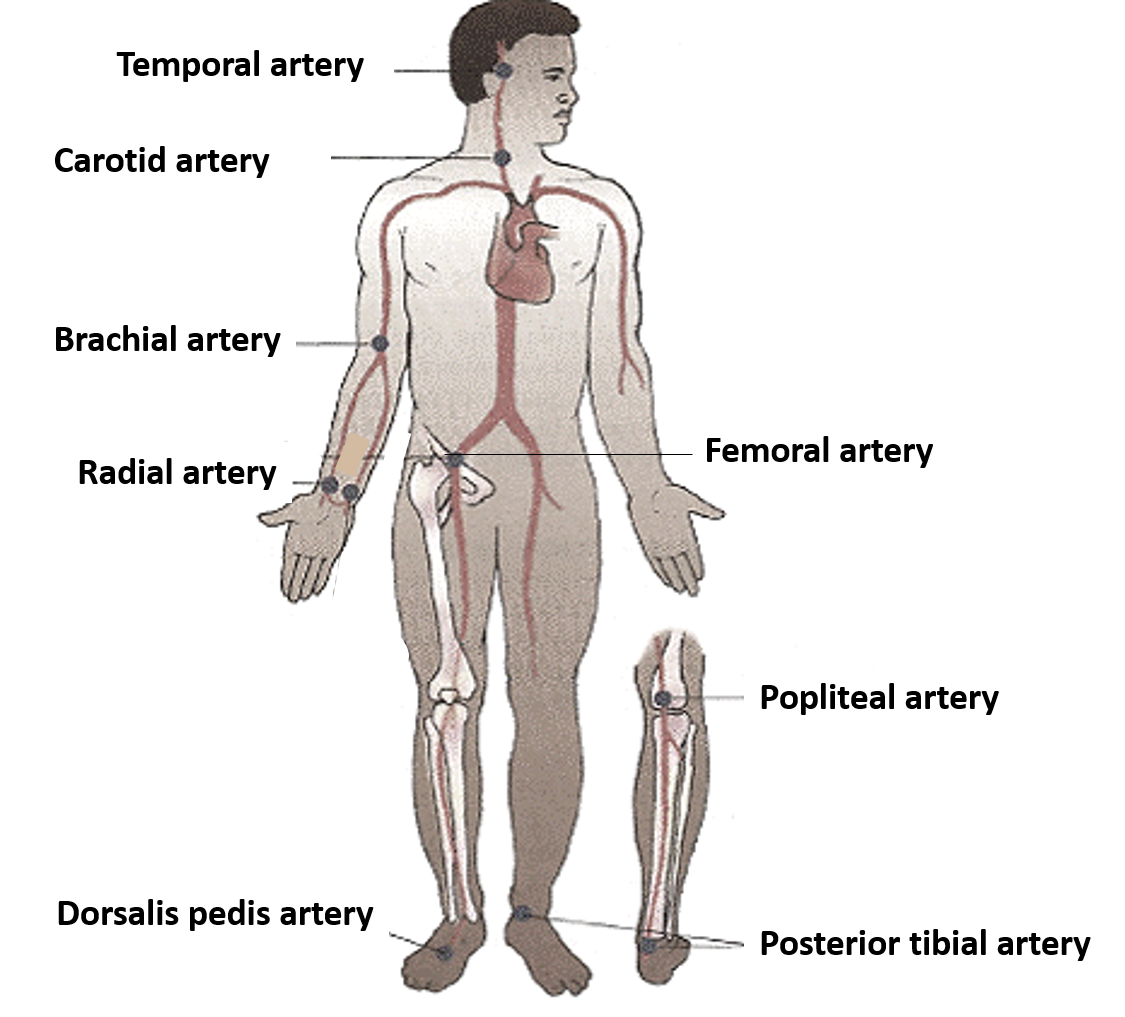
Name the Sites Where Arterial Pulsations can be Felt.
Following are the sites where arterial pulsations can be felt:
• Carotid artery – along the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle at the level of cricoids cartilage.
• Brachial artery – In front of the elbow medial to the tendon of biceps brachii.
• Radial artery – lateral side of front of forearm at wrist
• Femoral artery – below the inguinal ligament at midinguinal point
• Popliteal artery – in the popliteal fossa
• Dorsalis pedis artery – on the dorsum of foot between the tendon of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus.
What are the Factors that Help in Venous Return?
Factors that help in venous return are:
• Contraction of muscles
• Presence of valves in the veins
• Negative intrathoracic pressure
• Pulsation of arteries

Learning is taking place